HUMAN EXCRETORY SYSTEM
HUMAN EXCRETORY SYSTEM
Life of every organism depends on certain basic processes. Excretion is one among them. Different organisms follow different modes of excretion. In complex organisms including humans, there is a specialized system for excretion called human excretory system.
We all obtain our nutrients from different sources which are later digested and metabolized in our body. After metabolic reactions, the body starts to sort out useful and toxic substances in an individual. As we all know, the accumulation of the toxins may be harmful and the body removes all the metabolic wastes by the process called excretion.
Different organisms follow different modes of excretion such as kidney, lungs, skin and eyes depending on their habitat and food habit.
For example- Aquatic animals excrete waste in the form of ammonia, while birds and insects excrete mainly uric acid. Humans produce urea as the major excretory product.
Excretory System Organs
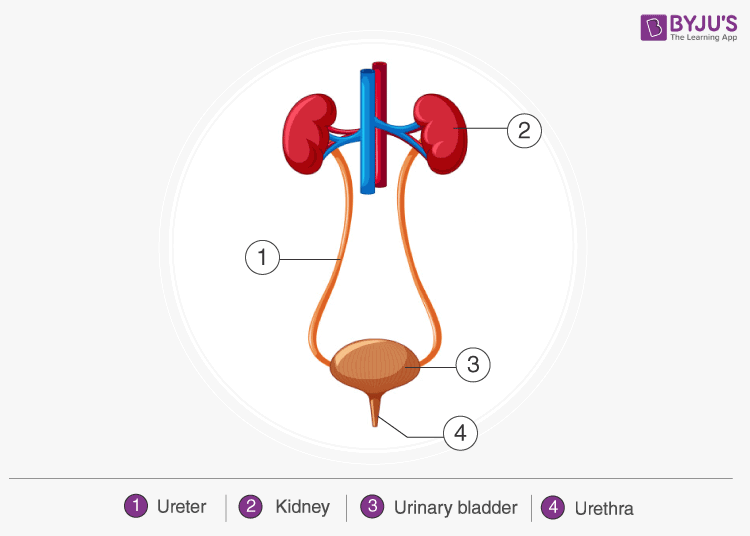
The human excretory system organs include:
- A pair of kidneys
- A pair of ureters
- A urinary bladder
- A urethra
Kidneys
Kidneys are bean-shaped structures located on either side of the backbone and are protected by the ribs and muscles of the back. Each human adult kidney has a length of 10-12 cm, a width of 5-7 cm and weighs around 120-170g.
The kidneys have an inner concave structure. The blood vessels, ureter and nerves enter the kidneys through the hilum, which is a notch at the inner concave surface of the kidney. The renal pelvis, a large funnel-shaped space is present inner to the hilum, is has many projections known as calyces.
Structure of Kidney
The structure of the kidney is explained below:
Capsule
The outer layer is called the capsule. Inside the kidney, there are two zones- the outer zone is the cortex and the inner zone is the medulla. The cortex extends in between the medullary pyramids as renal columns called columns of Bertin.
Nephrons
Nephrons are the functional units of the kidney. Each nephron has two parts- glomerulus and renal tubule.
Glomerulus consists of a bunch of capillaries formed by afferent arterioles. Blood from glomerulus is carried away by efferent arterioles.
The renal tubule starts with a cup-like structure called Bowman’s capsule and this encloses the glomerulus. The malpighian body consists of glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule. The highly coiled structure in the tubule next to the Bowman’s capsule is the proximal convoluted tubule.Explore more: Nephrons
Henle’s loop
The next part of the tubule is Henle’s loop which has an ascending and a descending limb. The ascending loop continues as a distal convoluted tubule. The distal convoluted tubules of many nephrons open into the collecting duct.
The cortical region of the kidney comprises of malpighian corpuscle, proximal convoluted tubule and distal convoluted tubule and the medullary region contains a loop of Henle.
There are two types of nephrons – cortical and juxtamedullary. In the case of cortical, the loop of Henle is very short and extends only a little into the medulla. In juxtamedullary, the loop of Henle is very long and runs deep into the medulla.Ureter
A pair of thin muscular tubes called the ureter comes out of each kidney extending from the renal pelvis. It carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
Urinary Bladder
It is a muscular sac-like structure, which stores urine. The urinary bladder is emptied by the process of micturition, i.e. the act of urination.
Urethra
This tube arises from the urinary bladder and helps to expel urine out of the body. In males, it acts as the common route for sperms and urine. Its opening is guarded by sphincter muscles.
Human Excretory System Diagram
The diagram below represents the different parts of the human excretory system.
Excretion in Humans
Excretion is the process where all the metabolic wastes are removed from the body. Excretion in humans is carried through different body parts and internal organs in a series of processes.Diffusion is the most common process of excretion in lower organisms. A human body is an exceptional machine, where different life-processes (respiration, circulation, digestion, etc.) take place simultaneously. As a result, many waste products produced in our body are in various forms that include carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogenous products like urea, ammonia, and uric acid.In addition to these, the chemicals and other toxic compounds from medications and hormonal products are also produced. Simple diffusion is not sufficient to eliminate these wastes from our body. We need more complex and specific processes in order to eliminate waste products.Blood contains both useful and harmful substances. Hence, we have kidneys which separate useful substances by reabsorption and toxic substances by producing urine.Kidney has a structural filtration unit called nephron where the blood is filtered. Each kidney contains a million nephrons.Capillaries of kidneys filter the blood and the essential substances like glucose, amino acids, salts, and the required amount of water get reabsorbed and the blood goes into circulation.Excess water and nitrogenous waste in humans are converted to urine. Urine thus produced is passed to the urinary bladder via the ureters. The urinary bladder is under the control of the Central Nervous System. The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine.Mechanism of Excretion in Humans
The process of excretion in humans takes place in the following steps:
Urine Formation
The urine is formed in the nephrons and involves the following steps:
Glomerular Filtration
Tubular Reabsorption
Secretion
Glomerular Filtration
It is the primary step in urine formation. In this process, the excess fluid and waste products from the kidney are filtered out of the blood into the urine collection tubules of the kidney and eliminated out of the body.
The amount of filtrate produced by the kidneys every minute is known as Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR).
Tubular Reabsorption
It is the absorption of ions and molecules such as sodium ions, glucose, amino acids, water etc. Water involves passive absorption, while glucose and sodium ions are absorbed by an active process.
Secretion
Potassium ions, hydrogen ions, and ammonia are secreted out to maintain the equilibrium between the body fluids.
The functions of the various tubules involved in the process are:
Glomerulus- filters the blood
Proximal Convoluted Tubules (PCT)- reabsorb water, ions and nutrients. They remove toxins and help in maintaining the ionic balance and pH of the body fluids by secretion of potassium, hydrogen and ammonia to filtrate and reabsorbing bicarbonate ions from the filtrate.
Descending Loop of Henle- is permeable to water and the filtrate gets concentrated as it is impermeable to electrolytes.
Ascending Loop of Henle- it is impermeable to water and permeable to electrolytes. The filtrate gets diluted due to the movement of electrolytes from the filtrate to the medullary fluid.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)- allows reabsorption of water and sodium ions. It also helps in maintaining pH and ionic balance by secretion and reabsorption of ions like PCT.
Collecting Duct- a large amount of water is reabsorbed from the filtrate by the collecting duct.
Micturition
The urinary bladder is stretched and gets filled with urine formed in the nephrons. The receptors present on the walls of the urinary bladder send signals to the Central Nervous System, thereby, allowing the relaxation of sphincter muscles to release urine. This is known as micturition.
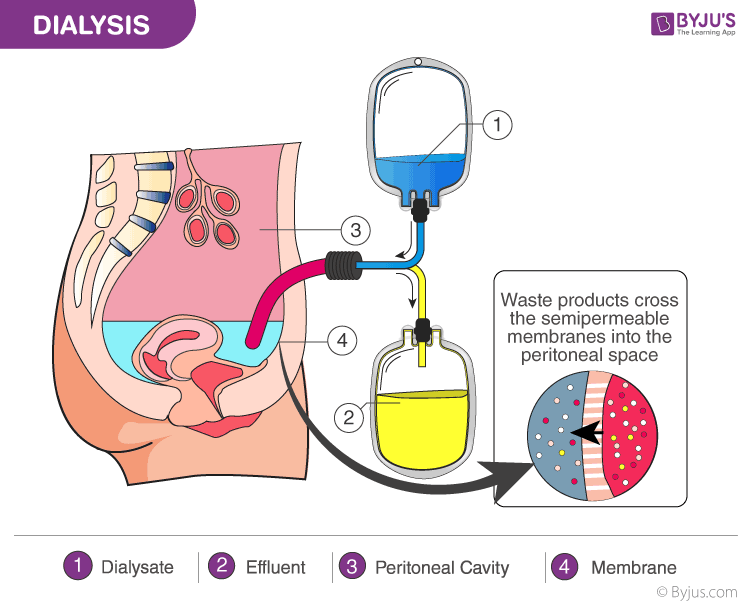
Dialysis

Comments
Post a Comment